Sinopse
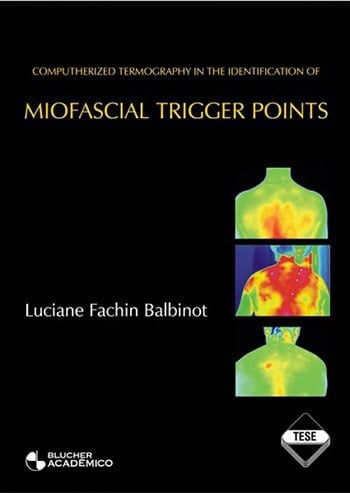
Computerized thermography, system with ability to capture the infrared light emissivity of any reflexive surface, is part of the current arsenal of instrumentation in biomechanics. Using this methodology, it is possible to assess the physiology of thermical maintenance through its skin surface representation. The aim of this work is to assess the thermography as the identification method of myofascial trigger points, been chosen the trapezius muscle as study focus since it is one of most affected body regions concerning myofascial syndrome. This syndrome is highly prevalent and historically sub-diagnosticated as it requires expert professionals to establish its diagnostic, through physical examination. The participants of this study were gathered as a sample of thirty persons, fifteen men and fifteen woman, ages between twenty three and seventy years (32,5 years in average). The algometry by pressure, highly validated method on previous works, has been used as part of physical examination to confirm the thermography events. The equipment used to collect the thermograms was an infrared camera with digital image processing, with thermical sensitivity for spectral ranges from 7 to 12 micrometers, appropriate for medical diagnostic utilization; the error index for measurement on this equipment is either 2% or 2oC. It has been used a dynamometer, clock type, for the algometry, commercially available for clinical use, which makes it possible to assess the applied pressure to the focal point. The trigger point identification was based in a pain diagram filled by the own subject using previously validated parameters. The imaging assessment was done using a deive analysis, having been taking in consideration the thermographic event corresponding to the trigger point, the hot spot or a discoid shaped surface, with one or more degrees Celsius hotter if compared to the neighbor reference point. Algometry was used in this work as reference method. Deive statistics were applied to assess sensibility and specificity in trapezius Myofascial Syndrome diagnoses. A totality of 250 trigger points had been founded: 198 (79.20%) identified by algometry and thermography; 41 points (16.40%) by thermography only; 11(4.40%) identified by algometry only. It was concluded that the thermograpy is an appropriated method for Myofascial Syndrome diagnostic on trapezius muscle.
Luciane Fachin Balbinot
Graduação em Medicina pela Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul (1989), com especialização em Fisiatria e Medicina do Trabalho pela UFRGS e Eletroneuromiografia pelo CFM. Mestrado em Ciências do Movimento Humano-Biomecânica, na UDESC, em novembro/2006.
Saiba maisDetalhes do livro
- Tipo: Livro Impresso
- ISBN: 9788561209803
- Acabamento: Brochura
- Total de Páginas: 132 páginas
- Ano da Edição: 2009
- Peso: 0.28 kg